What is Wireshark?
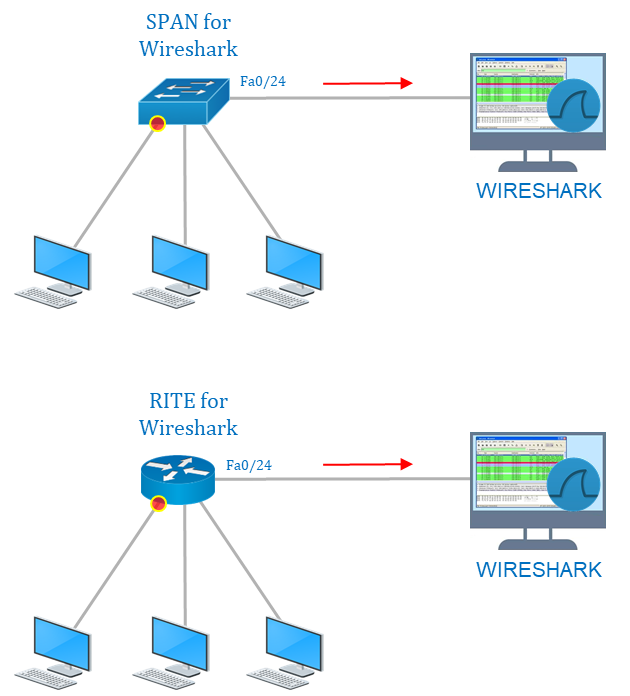
Wireshark is an open-source free packet sniffer and analysis network troubleshooting tool. It captures network traffic on the local network and stores that data for offline analysis. Wireshark can be set up in software form for local traffic of servers/computers. For network setup, we need to enable a port mirroring solution to send all traffic where the Wireshark terminal is connected as shown in this diagram.
Uses of Wireshark (network troubleshooting tool)
The uses of Wireshark are: It can be used by network engineers to examine security problems. It is used by network engineers to troubleshoot network issues. It also helps to troubleshoot latency issues and malicious activities on your network. It can also analyze dropped packets. It helps us to know how all the devices like laptops, mobile phones, desktops, switches, routers, etc, communicate in local network or the reset of the world
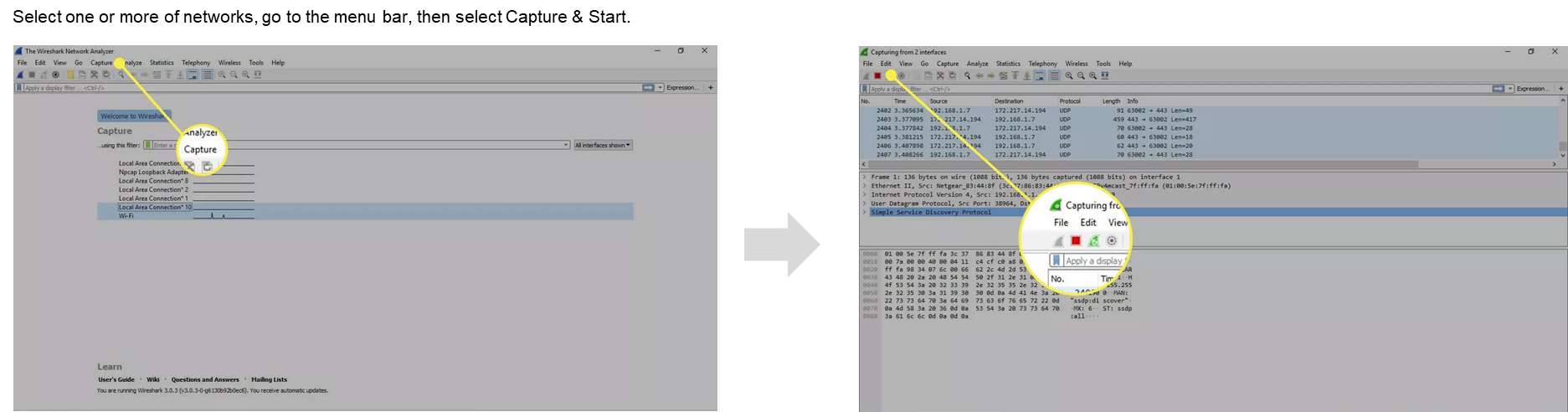
How to download and set up Wireshark
- Download Wireshark free from the official website: https://www.wireshark.org/download.html
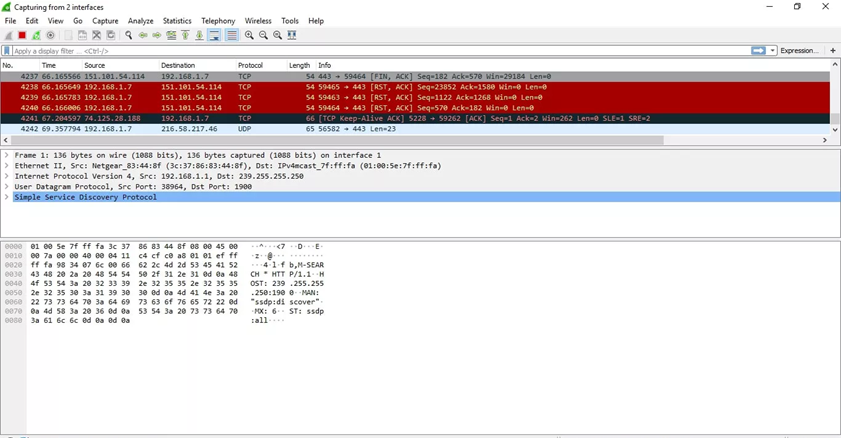
How to View and Analyze Packet Contents
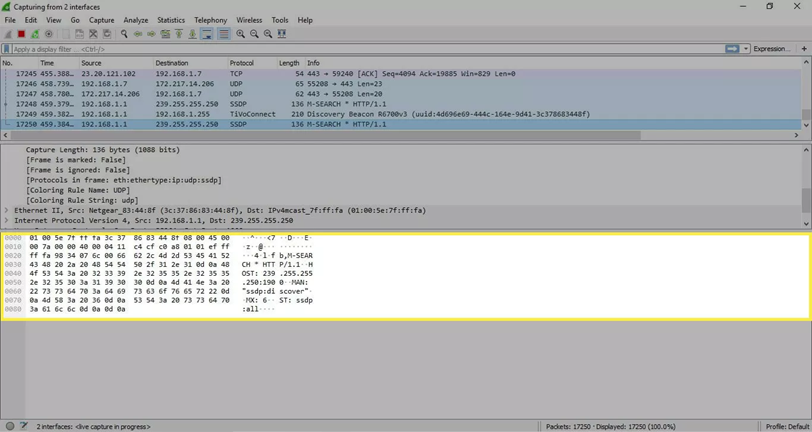
The captured data interface contains three main sections: the packet list pane (the top section), the packet details pane (the middle section), and the packet bytes pane (the bottom section)
1.
No: This field indicates which packets are part of the same conversation. It remains blank until you select a packet.
2.
Time: The timestamp of when the packet was captured is displayed in this column. The default format is the number of seconds or partial seconds since this specific capture file was first created.
3.
Source: This column contains the address (IP or other) where the packet originated.
4.
Destination: This column contains the address to which the packet is being sent.
5.
Protocol: The packet’s protocol name, such as TCP, can be found in this column.
6.
Length: The packet length, in bytes, is displayed in this column.
7.
Info: Additional details about the packet are presented here. The contents of this column can vary greatly depending on packet contents.
Packet Types
At the bottom is the packet bytes pane, which displays the raw data of the selected packet in a hexadecimal view. This hex dump contains 16 hexadecimal bytes and 16 ASCII bytes alongside the data offset.
Selecting a specific portion of this data automatically highlights its corresponding section in the packet details pane and vice versa. Any bytes that cannot be printed are represented by a period
Wireshark Filters
- Capture Filters: Capture filters are used to select which packets should be saved to disk while capturing
- Display Filters: Display filters are used to select what you want to see or analyze after capturing
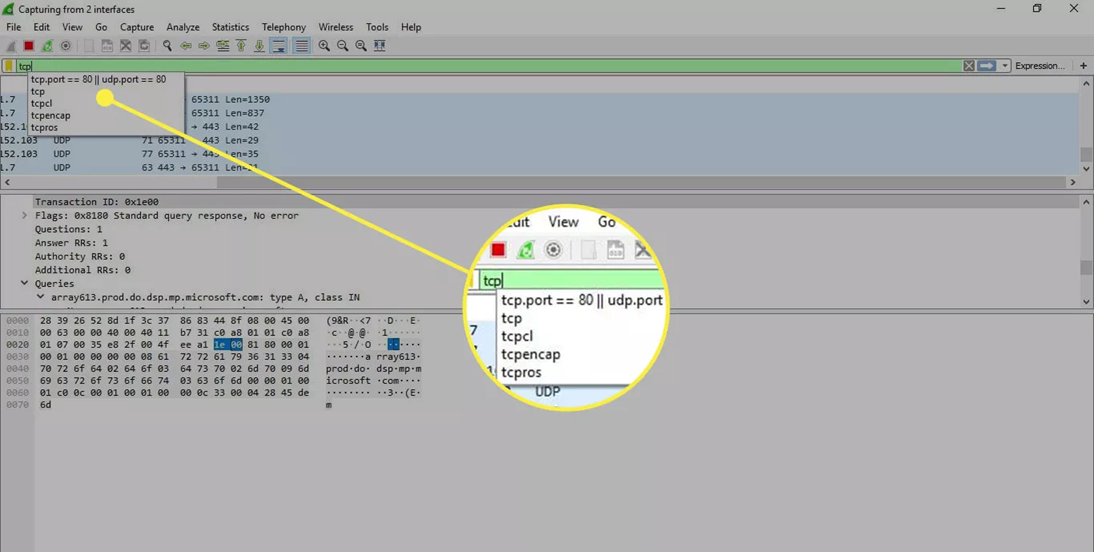
Wireshark provides a large number of predetermined filters by default. To use one of these existing filters, enter its name in the Apply a display filter entry field located below the Wireshark toolbar or in the Enter a capture filter field located in the center of the welcome screen.
For example, if you want to display TCP packets, type the Wireshark autocomplete feature that shows suggested names as you begin typing, making it easier to find the correct moniker for the filter you’re seeking.
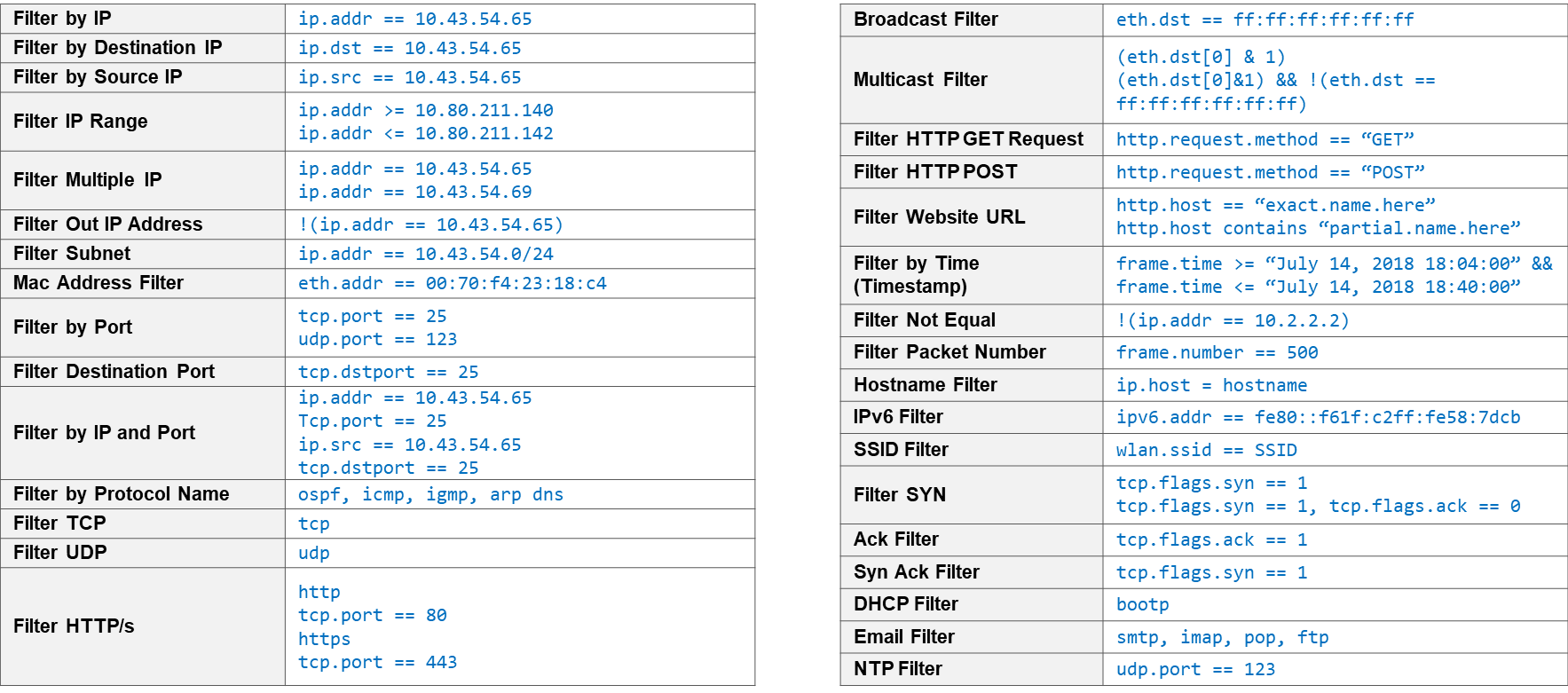
Below are some important Wireshark Filters:
-End-
You might also be interested in our free Online Quizzes on all IT topics including Cisco CCNA, Cyber Security, Python Programming, Linux & Ethical Hacking:
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)
You can also view free study notes (Cheat sheets) for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary Cheatsheets







