Layer-2 Port Security is used for network traffic control. It allows only the authorized user or filtered MAC address configured to gain access to the network.
Enabling mode Pass/Secret in Port Security
To enable mode Pass/Secret we have to Secure the Privileged Mode Access. An encrypted Password is recommended (enable secret)
Example of How to Enable mode Pass/Secret
Below is an example of how to enable mode Pass/Secret on the IOS Command Line Interface:
R1(config)# enable password
networkwalks
R1(config)# enable secret
networkwalks
Secure the Console (local Access)
Secure the Local access by adding a password to Console Line Access
Example of Securing the Console (Local Access)
Below is an example of how to secure the console with commands:
R1(config)# line console 0
R1(config)# login local
R1(config-if)# password
networkwalks
Secure the Telnet/SSH/vty (Remote Access)
In order to secure Telnet/SSH/vty we must Secure the Remote access by adding a password to Telnet/ssh/vty Line Access and always prefer SSH to Telnet because it’s more secure than Telnet
Example of How Telnet is Secured
Below is an example of how to secure Telnet through commands:
R1(config)# line vty 0 15
R1(config)# login local
R1(config-if)# password
networkwalks
Example of How SSH is Secured
The following is an example of how to secure SSH through commands:
R1(config)# line vty 0 15
R1(config-if)# transport input ssh
R1(config-if)# login local
R1(config)# crypto key generate rsa
Configure Privilege Levels
To configure Privilege Levels we have to always assign the minimum Privilege Levels to users according to their roles and a total of 16x Privilege Levels (0-15) in cisco devices
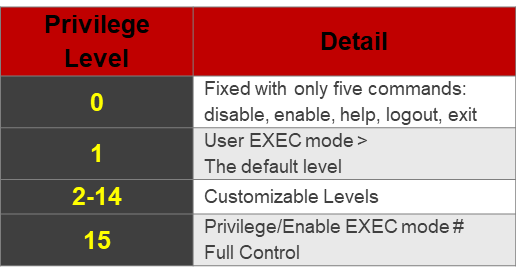
Example of Privilege Levels Configuration
Below is an example of Privilege Levels Configuration:
R1(config)# username
ARMAN privilege 15 password
networkwalks
Why we need to Configure Port Security in Networking
Always configure Port Security on Switches to secure Physical Access (accept only allowed no. of devices, learn the MAC addresses of those devices dynamically & block traffic from invalid hosts if a violation occurs)
Example of How Port Security in Networking is Configured
Below is an example of how to configure security on Ports:
SW1(config)#interface fa0/1
SW1(config-if)#switchport mode access
SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security
SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 2
SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address 0000.0000.1111
Why do we need to Shutdown Un-used Ports in Port Security?
It is always recommended to shutdown un-used Ports & place them in un-used VLAN other than default vlan1 (although it’s a common practice to keep Router ports shutdown while Switch ports open)
Example of How to Shutdown Un-used Ports in Port Security
Below is an example of how shutdown Un-used Ports on the IOS Command Line Interface:
SW1(config)# interface range fa0/3-24
SW1(config-if)# shutdown
SW1(config-if)# switchport mode access
SW1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 99
-End-
You might also be interested in our free Online Quizzes on all IT topics including Cisco CCNA, Cyber Security, Python Programming, Linux & Ethical Hacking:
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)
You can also view free study notes (Cheat sheets) for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary Cheatsheets
 Layer-2 Port Security is used for network traffic control. It allows only the authorized user or filtered MAC address configured to gain access to the network.
Layer-2 Port Security is used for network traffic control. It allows only the authorized user or filtered MAC address configured to gain access to the network.

