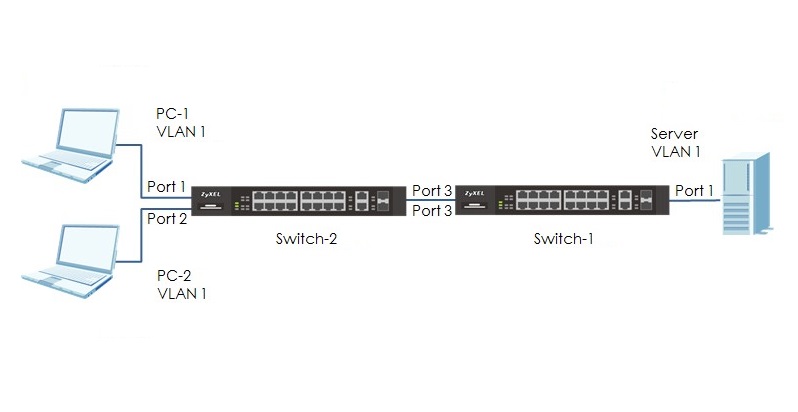
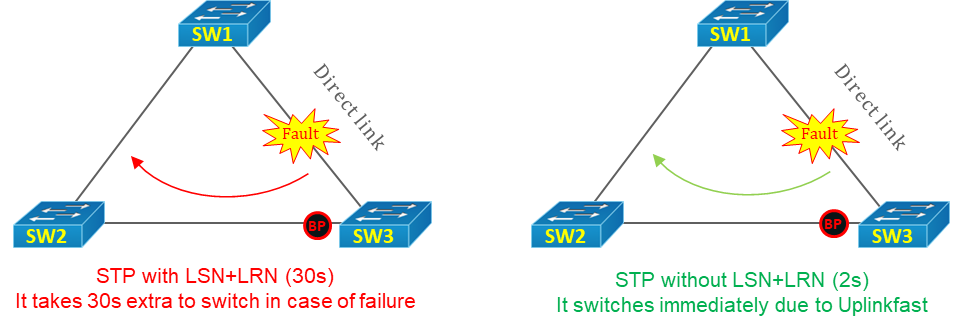
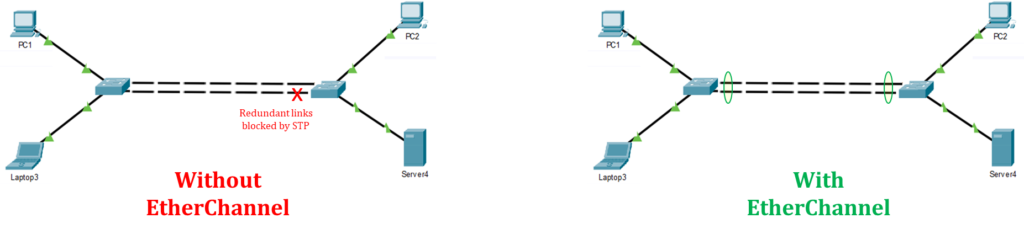
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical grouping of network devices within a local area network (LAN) that allows devices to communicate as if they were on the same physical LAN, even if they are physically located on different segments. VLANs have become essential for network administrators to design efficient, secure and manageable networks. VLANs allow network segmentation, creating virtual networks within a physical infrastructure. This article delves into what VLANs are, why they are important and how to configure them, especially for those preparing for Cisco’s CCNA certification. What is a VLAN? A VLAN is actually Read More …