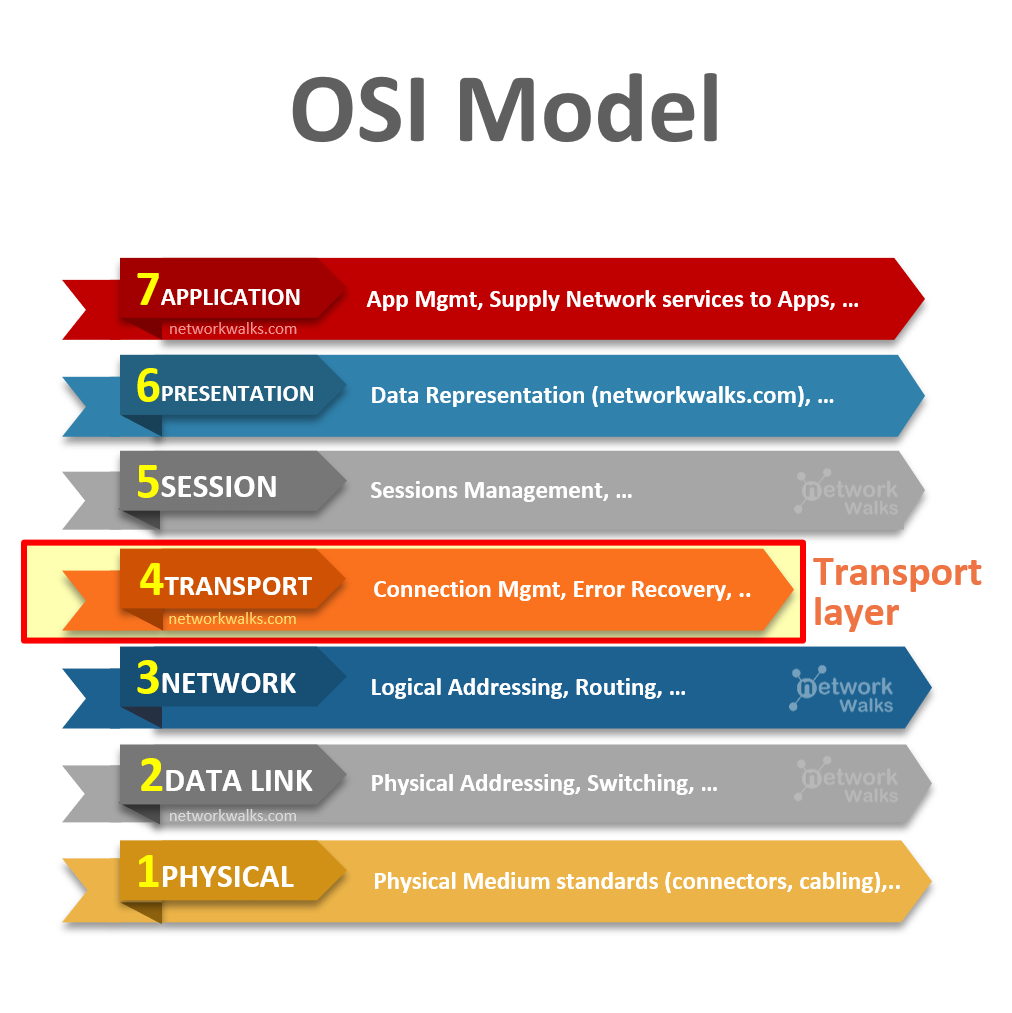
 Transport Layer is the fourth layer in 7 Layer OSI Model after Network Layer. Similar to Layer-2 and Layer-3, this layer also performs addressing & multiplexing but in different domain through TCP and UDP.
OSI Model divides the network communication processes into seven layers in order to simplify it. Each layer performs specific functions to support the layers above it. The seven Layer model starts from Physical till Application Layer & Transport layer is in the middle. The core concept behind Transport layer is the “support of Multitasking”. It allows same computer, browser & internet connection to work on multiple applications simultaneously & this is achieved through Port Numbers, Transport Layer Addressing & Multiplexing. Below figure shows the position of Data Link layer in the OSI Model:
Transport Layer is the fourth layer in 7 Layer OSI Model after Network Layer. Similar to Layer-2 and Layer-3, this layer also performs addressing & multiplexing but in different domain through TCP and UDP.
OSI Model divides the network communication processes into seven layers in order to simplify it. Each layer performs specific functions to support the layers above it. The seven Layer model starts from Physical till Application Layer & Transport layer is in the middle. The core concept behind Transport layer is the “support of Multitasking”. It allows same computer, browser & internet connection to work on multiple applications simultaneously & this is achieved through Port Numbers, Transport Layer Addressing & Multiplexing. Below figure shows the position of Data Link layer in the OSI Model:
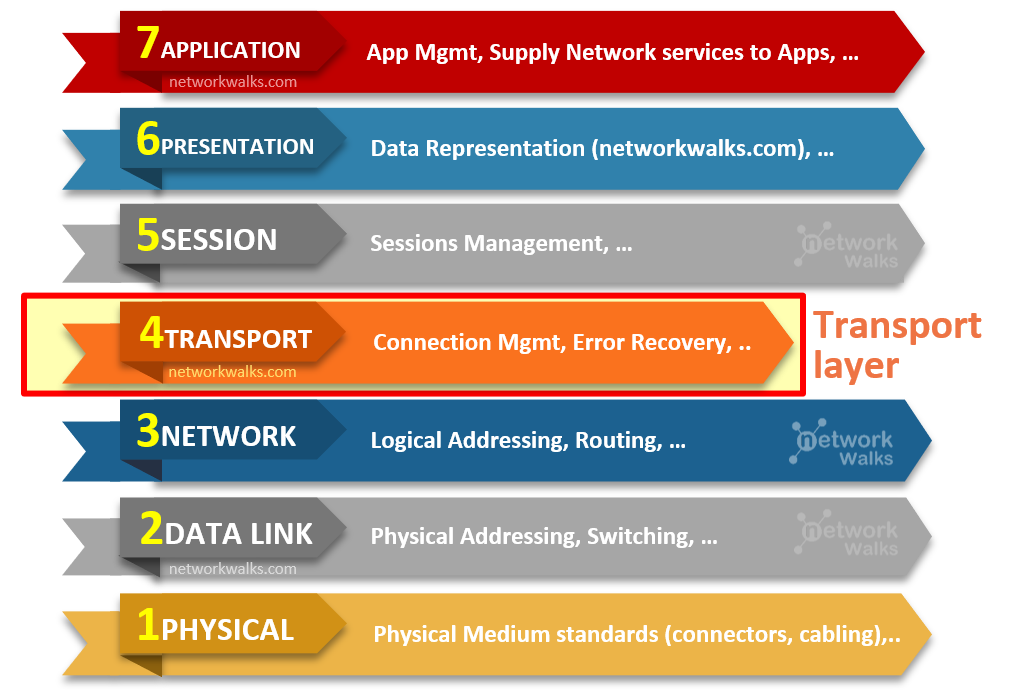 Transport layer is in the middle of the OSI Model as in below figure. It is a part of both the lower and upper of layer groups.
Lower layers, because it is involves the transport of data,
Upper Layers, because its functions are also somewhat high-level.
PDU at Transport Layer is called Segment.
Transport layer is in the middle of the OSI Model as in below figure. It is a part of both the lower and upper of layer groups.
Lower layers, because it is involves the transport of data,
Upper Layers, because its functions are also somewhat high-level.
PDU at Transport Layer is called Segment.
Functions/Duties of Transport Layer
Each Layer in OSI Model Performs some important duties. Important functions performed by Transport Layer are listed here:- Sequencing: Sequencing is a connection-oriented service that takes TCP segments that are received out of order and place them in the right order
- Error Control: Is uses error control mechanisms to ensure reliable delivery of data. Due to this acknowledgement mechanisms, the receiver can detect how many bits have been corrupted during transmission. Receiver then requests the sender to send those bits again to ensure that no data is lost during transmission.
- Other Functions of Transport Layer include: End to End Connection Management, Transmission, Segmentation and Flow Control
- Transport Layer is responsible for Layer-4 Addressing which is also called Process Level Addressing. It allows a computer to use multiple network layer protocols simultaneously.
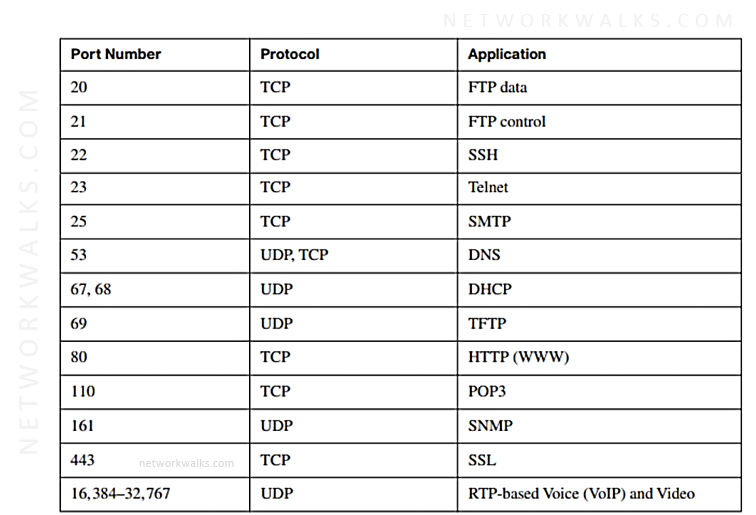
|
Transport Layer Ports |
||
| Category | Range | Comments |
| Well Known Ports | 0 – 1023 | Used by system processes e.g. FTP(21), Telnet(23), HTTP(80)… |
| Registered Ports | 1024 – 49151 | Assigned by IANA for specific services upon application by a requesting entity. e.g. Port 8080 |
| Private Ports | 49152 – 65535 | Used for Private purposes & are not registered with IANA. |
Transport Layer Protocols
The OSI Model provides a conceptual framework for communication between computers, but the model itself is not a method of communication. Actual communication is made possible by using communication protocols. Each layer on the OSI Model has some protocols associated with it. Some important protocols on Transport layer are listed in below:- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- SPX
- ESP
- Fiber Channel Protocol
- iSCSI
- SCTP
- GRE
- HSRP, VRRP, …
Network Equipment/Components at Transport Layer
- Firewalls
- Gateways
- Load Balancers
Summary
It is the 4th Layer in OSI seven layered Model. It performs important functions like Layer-4 Addressing, Multiplexing, Demultiplexing, Sequencing, Error Control, End to End Connection Management, Transmission, Segmentation & Flow Control. Important Protocols at Transport Layer include TCP, UDP, SPX, BGP, ESP, Fiber Channel Protocol, iSCSI and SCTP. Equipment operating at Transport Layer include Firewalls, Gateways and Load Balancers. PDU is called Segment.
Now, test your knowledge on OSI Model using our free Quizzes & Cheat sheet resources for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary Cheatsheets
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)Follow our Facebook Page & YouTube Channel for more updated Cheatsheets & Quizzes:
