
QoS (Quality of Service) is simply Traffic discrimination. QoS in Networking can also be defined as a set of technologies used to manage traffic and ensure the performance of critical applications. It enables firms or organizations to adjust their entire network by prioritizing certain high-performing applications.
Problems Solved by Quality of Service (QoS) in Networking
The problems that QoS solves are:
- It provides predictable management of network resources during times of congestion
- It helps in maximizing the end-user experience of critical sessions
- It provides differentiated services to packets based on pre-defined user criteria
Factors affected by Quality of Service (QoS) in Networking
The factors affected by QoS are Bandwidth, Delay, Jitter, and Data Loss (or Drops)
Forwarding PHB (per-hop behavior) for Quality of Service (QoS)
Forwarding per-hop behavior for QoS are grouped into the following: Classification, Marking, Queuing, Congestion, Policing, and Shaping
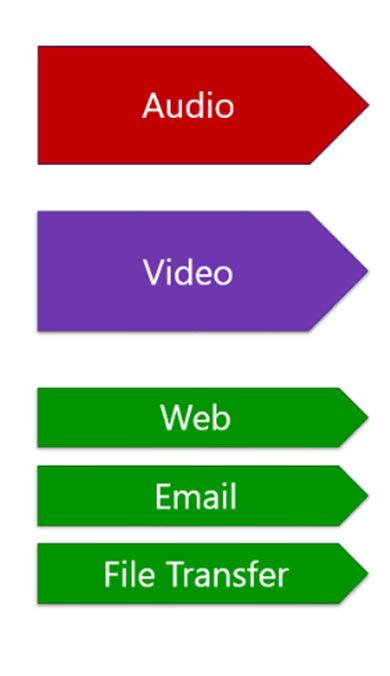
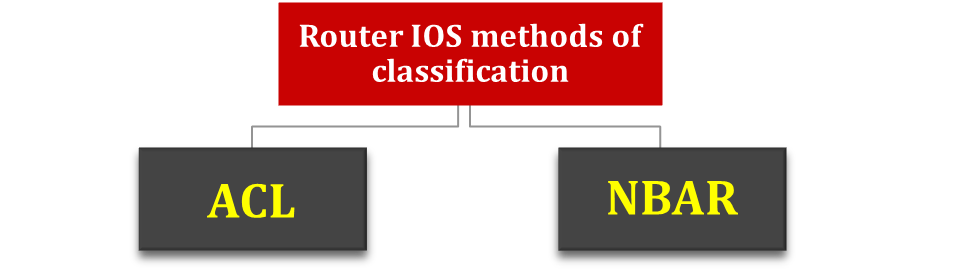
Classification
It is the process of matching the fields in a message to make a choice to take some QoS action
Marking
It gives critical traffic preferential treatment to make sure it is quickly and reliably delivered

Queuing
Managing the queues that hold packets while they wait for their turn to exit an interface
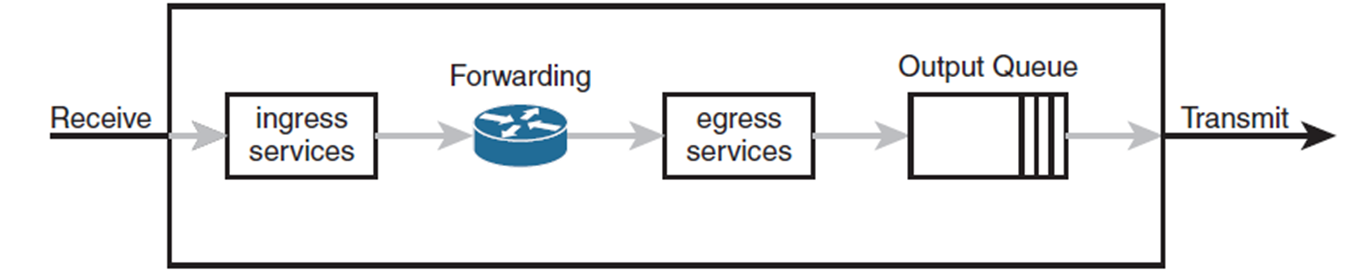
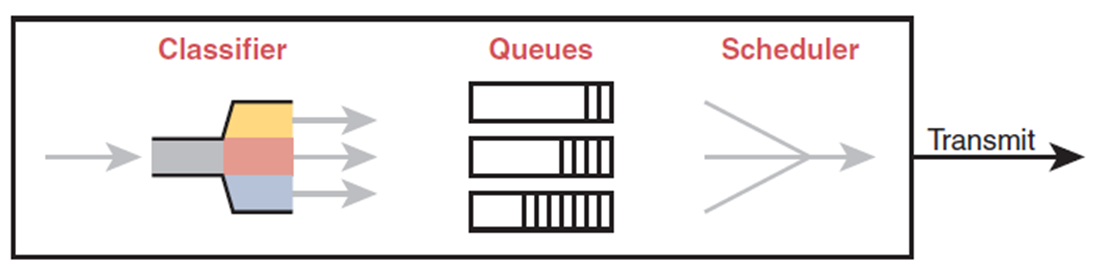
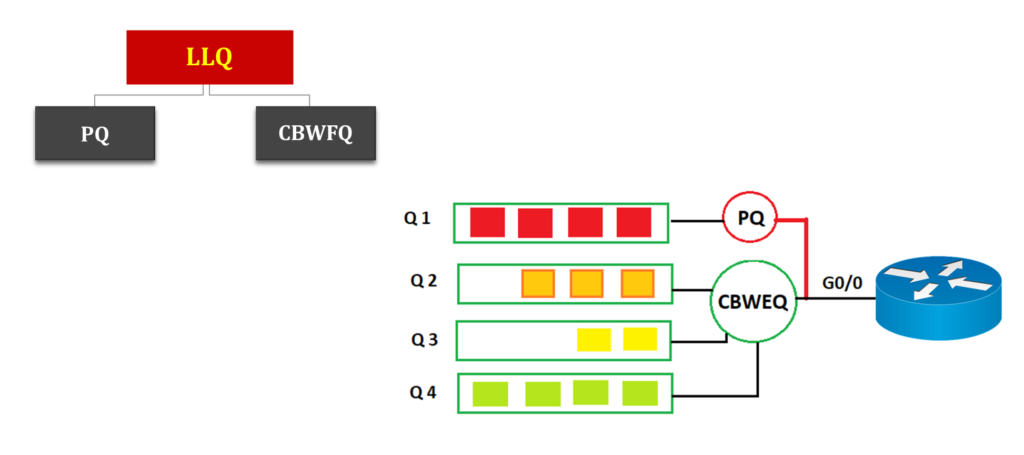
Congestion
It is a set of features to pre-emptively drop traffic within queues
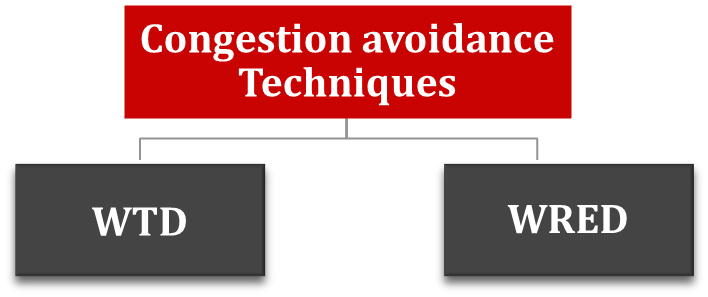
Policing
It is simply rate-limiting, as shown in below picture:
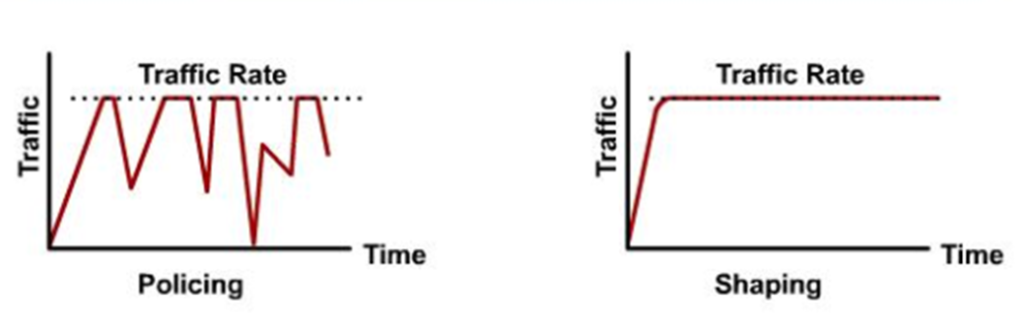
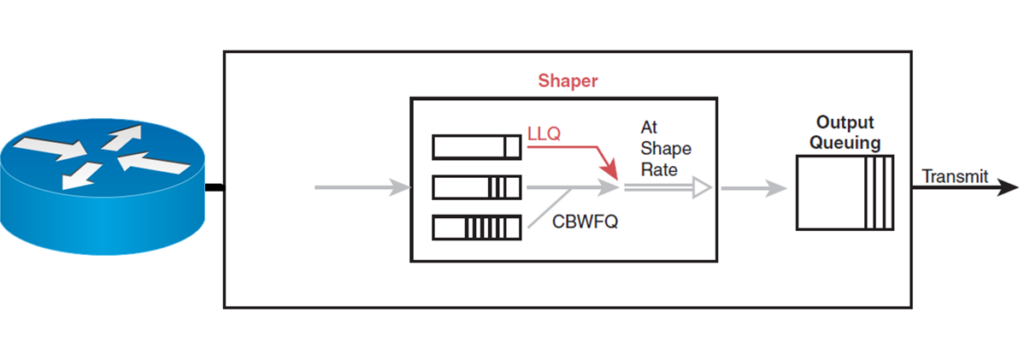
Shaping
It is simply the mechanism used to control the amount and the rate of traffic sent to the network
-End-
You might also be interested in our free Online Quizzes on all IT topics including Cisco CCNA, Cyber Security, Python Programming, Linux & Ethical Hacking:
QoS (Quality of Service) Quiz (Online) For CCNA
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)
You can also view free study notes (Cheat sheets) for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary Cheatsheets
 QoS (Quality of Service) is simply Traffic discrimination. QoS in Networking can also be defined as a set of technologies used to manage traffic and ensure the performance of critical applications. It enables firms or organizations to adjust their entire network by prioritizing certain high-performing applications.
QoS (Quality of Service) is simply Traffic discrimination. QoS in Networking can also be defined as a set of technologies used to manage traffic and ensure the performance of critical applications. It enables firms or organizations to adjust their entire network by prioritizing certain high-performing applications.










