 What is OSPF?
Open Shortest Path First is an open standard link state routing protocol which works by using Dijkastra’s SPF algorithm to find the shortest paths.
What is OSPF Router ID?
OSPF Router ID is an identifier which is used to identify the Router. It is a 32-bit number.
How does a Router select its OSPF Router ID?
Most of Routers (including Cisco) derive the Router ID in the following precedence order:
What is OSPF?
Open Shortest Path First is an open standard link state routing protocol which works by using Dijkastra’s SPF algorithm to find the shortest paths.
What is OSPF Router ID?
OSPF Router ID is an identifier which is used to identify the Router. It is a 32-bit number.
How does a Router select its OSPF Router ID?
Most of Routers (including Cisco) derive the Router ID in the following precedence order:
- Manually configured Router ID
- Highest Loopback Address
- Highest Physical IP Address on the Router
|
OSPF Timers (OSPF Intervals) |
||
|---|---|---|
| OSPF Network Type | Default Hello Interval | Default Dead Interval |
| Broadcast | 10 seconds | 40 seconds |
| Non-broadcast | 30 second | 120 seconds |
| Point-to-Point | 10 seconds | 40 seconds |
| Point-to-Multipoint | 30 seconds | 120 seconds |
| Point-to-Multipoint Non-broadcast | 30 seconds | 120 seconds |
| Loopback | N/A | N/A |
What are the OSPF network/Interface types? Below are the OSPF network/Interface types:networkwalks_R1(config)# router ospf 5networkwalks_R1(config-router)# router-id 5.5.5.5

- Protocol Type of OSPF: Link State
- Algorithm: SPF (Dijkstra’s)
- Type: IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol)
- Metric of OSPF: Cost (Bandwidth)
- Equal Cost Routes handling: CEF Load Balancing
- No. of packet types: 5
- Admin Distance: 110
- Reference BW: 108
- Standard: RFC2328 (OSPFv2), RFC2740 (OSPFv3/IPv6)
- Multicast Address: 224.0.0.5, 224.0.0.6
- Transport: IP (Port89) … refer to networkwalks website
- V-Link Support: YES
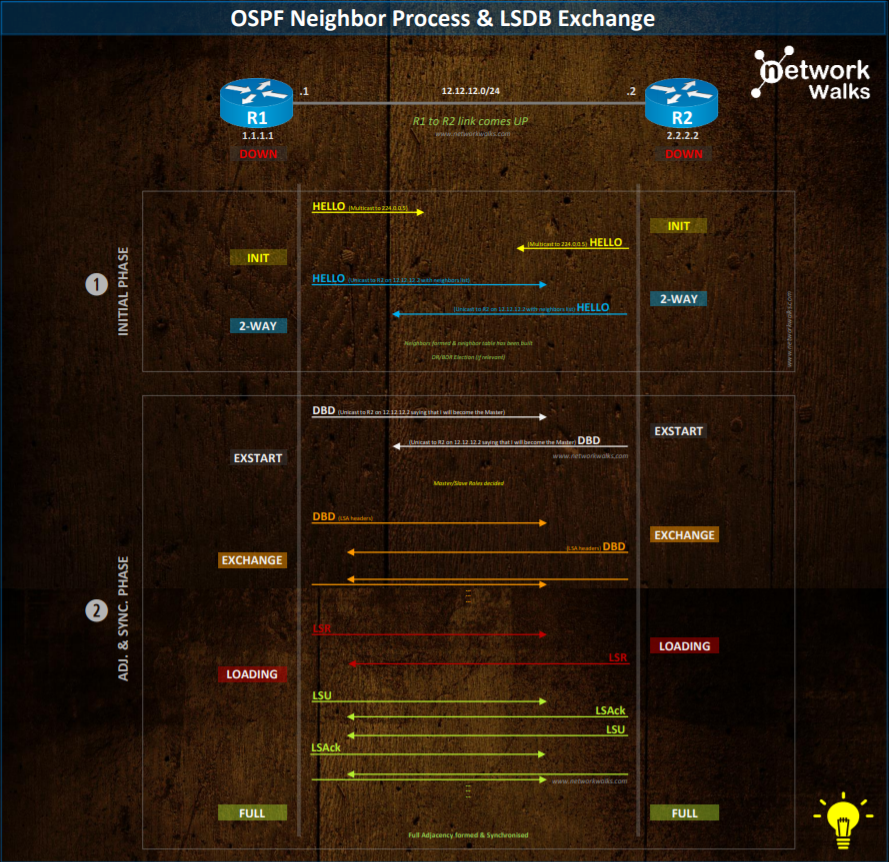
Two Routers in OSPF are called NEIGHBORS if they are exchanging Hello Packets. Two Routers in OSPF are called an ADJACENCY if they are exchanging Hello Packets as well as DatabaseWhat are the steps required to change Neighborship into adjacency? There are the steps required for a neighborship to change into adjacency:
- Two-way communication (using Hello Protocol)
- Database Synchronization which means exchange of Database Description (DD) packets, Link
- State Request (LSR) packets, Link State Update (LSU) packets
- After Database synchronization is complete, the two Routers are considered as adjacent
- Internal Routers (IR) = An OSPF Router whose all interfaces belong to the same area
- Backbone Routers (BR) = An OSPF Router which is Internal Router in Area 0
- Area Border Routers (ABR) = An OSPF Router which has interfaces in more than one area
- Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBR) = An OSPF Router which advertises external routes into the OSPF Domain
- LSA = Link State Advertisement
- LSU = Link State Update
- LSR = Link State Request
- OSPF Summarization reduces the amount of information stored in routing tables
- OSPF Summarization allocates an existing pool of addresses more economically
- OSPF Summarization reduces the load on Router processor and memory resources
- OSPF Summarization reduces number of update messages
- OSPF Summarization reduces the bandwidth usage
- High No. of Adjacencies
- Excessive LSA flooding
- Highest OSPF Interface Priority
- Highest Router ID (if OSPF interface priorities are equal)
- Router with the Second Highest OSPF Interface Priority
1 = Default Priority 0 = Means the Router will never become DR/BDRWhat is OSPF Virtual Link? OSPF requires the use of a backbone area (area 0) with each area connecting to area 0 through an Area Boundary Router (ABR). However, in some cases, regular area might not have a convenient point of connection to the backbone area. In this case, OSPF uses virtual link to connect that regular area to backbone area virtually. An OSPF virtual link allows two ABRs that connect to the same non-backbone area to form a neighbor relationship through that non-backbone area, even when separated by many other Routers and subnets. This virtual link acts like a virtual point-to-point connection between the two Routers, with that link inside area 0. The Routers form a neighbor relationship, inside area 0, and flood LSAs over that link. Can we change the reference bandwidth in OSPF? Yes, we can change the reference bandwidth using the OSPF auto-cost reference-bandwidth command. What is the value of OSPF reference Bandwidth? By default, reference bandwidth is 100 Mbps. The OSPF link-cost is a 16-bit number. Therefore, the maximum value supported is 65,535. What is the Link-State Retransmit (LSR) interval? OSPF must send acknowledgment of each newly received LSA. LSAs are retransmitted until they are acknowledged. The link-state retransmit-interval defines the time between retransmissions. We can use the command IP OSPF retransmit-interval to set the retransmit-interval. The default value is 5 seconds. How do you stop individual interfaces from developing adjacencies in an OSPF network? To stop Routers from becoming OSPF neighbors on a particular interface, issue the passive-interface command at the interface. For example:
Is it possible to have OSPF over a GRE tunnel? Yes, it is possible to have OSPF run over a GRE tunnel. What is an OSPF adjacency? An OSPF adjacency is a conceptual link to a neighbor over which Link State Advertisements (LSAs) can be sent. What are the five OSPF packet types? These are the five types of OSPF packets:networkwalks_R1(config)# router ospf 1networkwalks_R1(config-router)# passive-interface fa0/0
- HELLO
- DBD (Database Descriptor)
- LSR (Link State Request)
- LSU (Link State Update)
- LSAck (Link State Acknowledge)
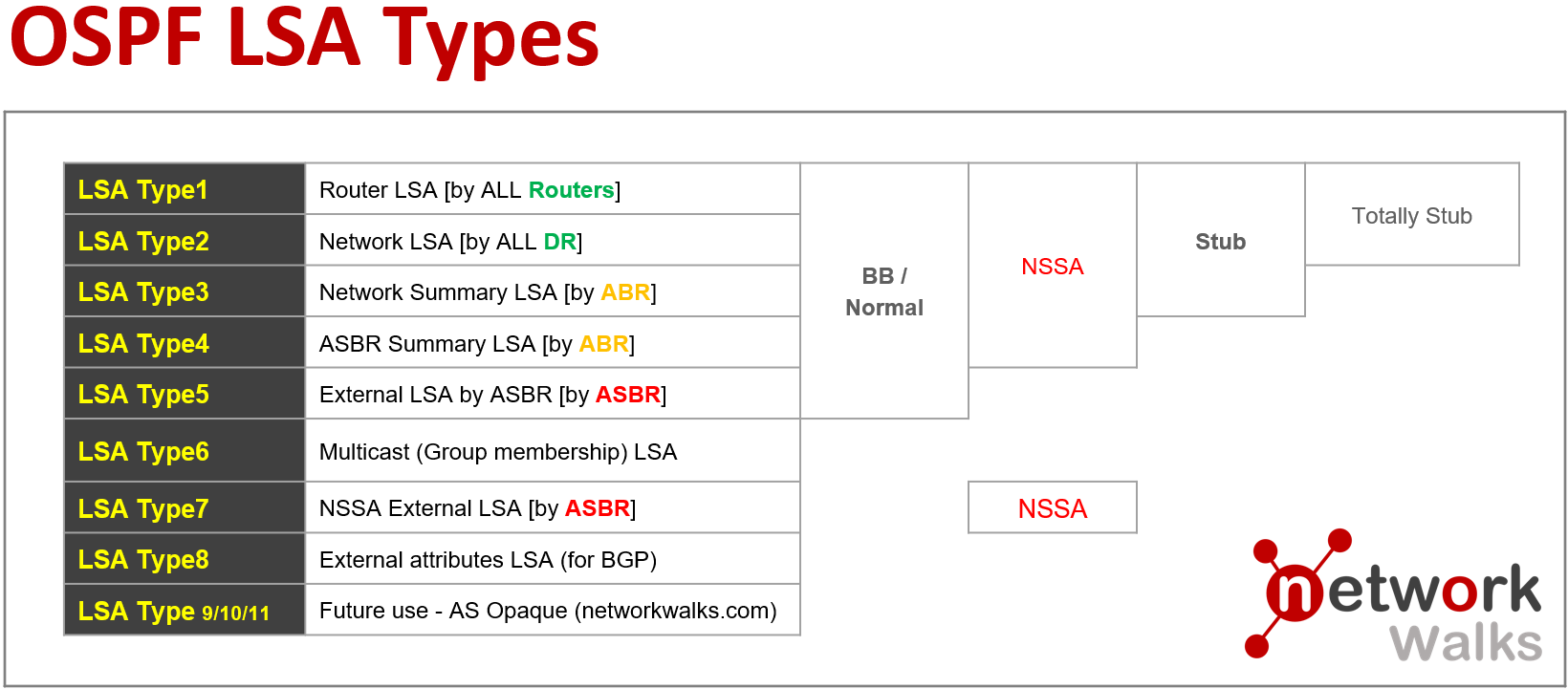
 What are different OSPF Link-State Advertisement (LSA) Types?
Below are the OSPF LSA Types:
What are different OSPF Link-State Advertisement (LSA) Types?
Below are the OSPF LSA Types:
 What is the order of preference for OSPF Route?
OSPF routes are selected in below preference order:
What is the order of preference for OSPF Route?
OSPF routes are selected in below preference order:
- Intra-Area OSPF routes (O)
- Inter-Area OSPF routes (OIA)
- External OSPF routes type-1 (OE1)
- External OSPF routes type-2 (OE2)
- NSSA1 (N1)
- NSSA-2 (N2)
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)You can also view free study notes (Cheat sheets) on all IT and Cisco CCNA/CCNP/CCIE topics for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary CheatsheetsFollow our Facebook Page & YouTube Channel for more updated Cheatsheets & Quizzes:

Good revision questions