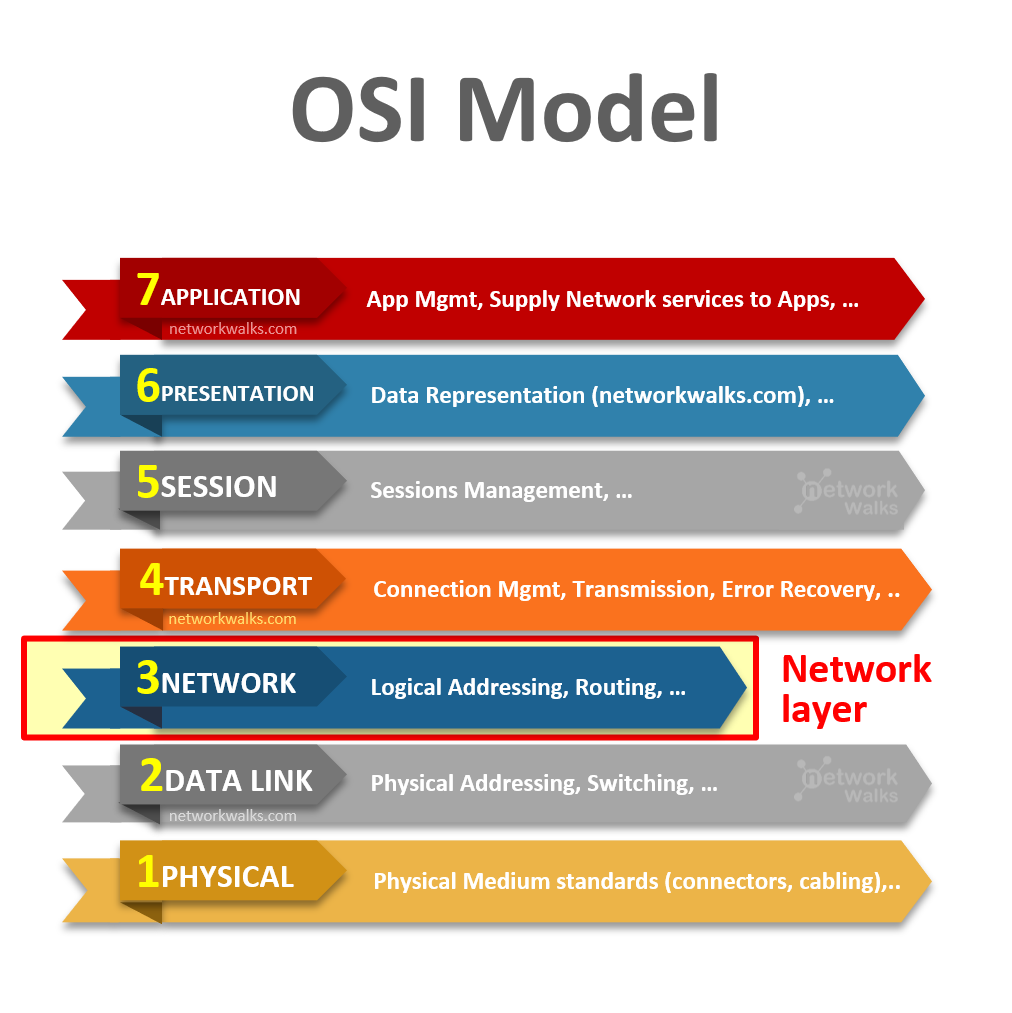
 Network Layer is the 3rd layer in 7-Layer OSI Model after Data Link Layer. This is the place where most Routing and network stuff resides. It controls the Logical boundaries of Network. Network Layer controls the operation in networking at routing layer. The main aim of this layer is to deliver packets from source to destination across multiple links or networks. If two computers or host systems are connected on the same link, then there is no need for a network layer.
Network Layer is the 3rd layer in 7-Layer OSI Model after Data Link Layer. This is the place where most Routing and network stuff resides. It controls the Logical boundaries of Network. Network Layer controls the operation in networking at routing layer. The main aim of this layer is to deliver packets from source to destination across multiple links or networks. If two computers or host systems are connected on the same link, then there is no need for a network layer.
Note: Most of the students & network engineers confuse Layer2 & Layer3. There is a basic difference between Network Layer & Data Link Layer. Network Layer is concerned with data transfer from one computer to another computer even if it is on a remote network, while the data link layer only deals with devices that are local to each other & are within one network. PDU at Data Link Layer is called Packet. OSI Model divides the network communication processes into seven layers in order to simplify it.
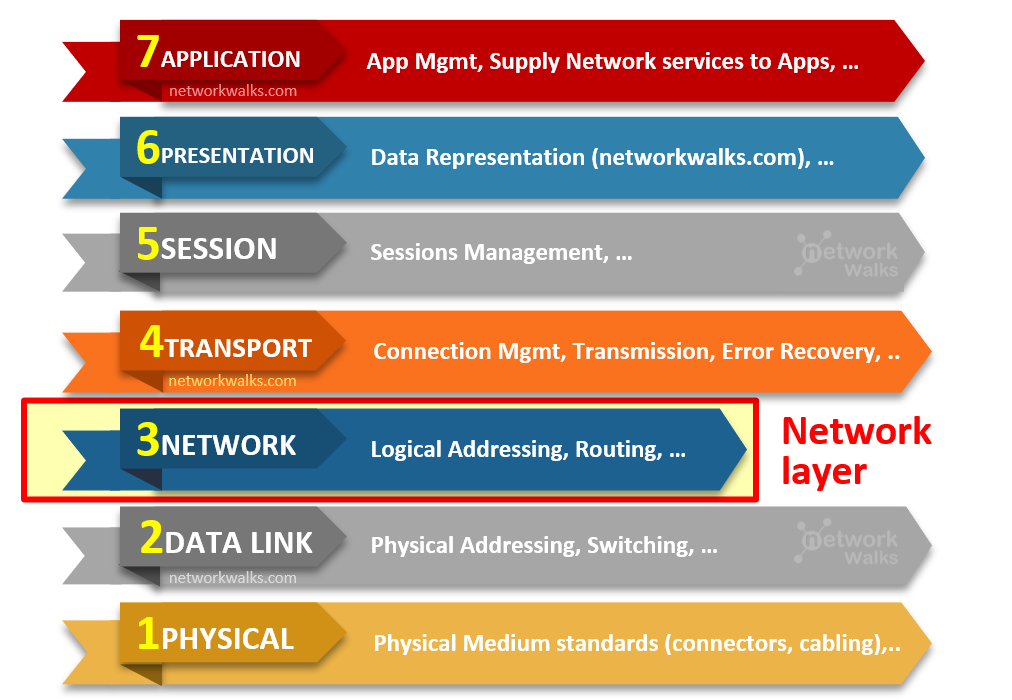
Functions/Duties of Network Layer
Each Layer in OSI Model Performs some important duties. Important functions performed by Network Layer are listed here:- Logical Addressing: Network layer is responsible for logical addressing. It assigns a unique ID to each device on Layer-3 network which we call IP Address. Network Layer processes the incoming packets, filters them & sends them to their desired destination
- Encapsulation: Network layer encapsulates Transport layer segments into Layer-3 Packets & forwards to Data Link Layer for further processing
- Fragmentation: Network layer is also responsible for fragmentation of packets to match the MTU size of Layer-2 frames
- Error Control: Error control and recovery also falls under the responsibilities & functions of Network Layer. Is uses error control mechanisms to ensure reliable delivery of data. Due to these acknowledgment mechanisms, the receiver can detect how many Layer-3 Packets have been corrupted during transmission. Receiver then requests the sender to send those Layer3 Packets again to ensure that no data is lost during transmission
Network Layer Protocols
The OSI Model provides a conceptual framework for communication between computers, but the model itself is not a method of communication. Actual communication is made possible by using communication protocols. Each layer on the OSI Model has some protocols associated with it. The most common protocol at Network Layer is of course the Internet Protocol which we know as IP. Other important Protocols at Network Layer include:- IPv4
- IPv6
- RIP
- RIP, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP
- ICMP
- IPSec
- IPX
- NAT
- GRE
- HSRP, VRRP, …
Equipment/Components at Network Layer
Similar to protocols, each layer has associated equipment with it. Some important Equipment that operate at Physical Layer of OSI Model are listed in below:- Routers
- Layer 3 Switches
Summary
Network layer is the 3rd Layer in seven layer OSI Model. It performs important functions like Logical Addressing, Routing, Encapsulation, Fragmentation & Error Control. Important Protocols at Network Layer include IPv4, IPv6, RIP, OSPF, BGP, ICMP, EIGRP, IPSec, IPX, NAT, GRE, HSRP & VRRP. Equipment operating at Network Layer include Routers & L3 Switches. PDU at network layer is called Packet.
Now, test your knowledge on OSI Model using our free Quizzes & Cheat sheet resources for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary Cheatsheets
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)Follow our Facebook Page & YouTube Channel for more updated Cheatsheets & Quizzes:
