“IP address is a unique number which is used to identify network devices in computer networks”.
An IP address mainly serves two functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. It is a logical numeric address that is assigned to every single computer, printer, switch, router or any other device that is part of a TCP/IP based network. The IP exists in every network, even only a pair of computers or a network of a large enterprise. Each computer, without exceptions, has its own unique address, if there is a connection to the network. Each of the computers in the network is related to IP. Moreover, there can not be two devices in one network with identical IP’s. But IP’s can be same in different networks.
IP’s as allocated step by step. Allocation starts with the request of the Internet provider to the national centers. They further distribute the received IP range of addresses among the customers. Customers can also become Internet service providers, in their turn, distributing the received IP’ss between their customers.
IP is like a phone number or your home address e.g. 1.1.1.1 or 192.168.0.1
IP Address Classification & Types
IP Address types can be classified in many ways including the Types of IP’s by Operation Method, by IP Versions, by Assignment Method, by Classes and by Visibility. Lets discuss each classification one by one.
A. Types of IP Address by Operation Method
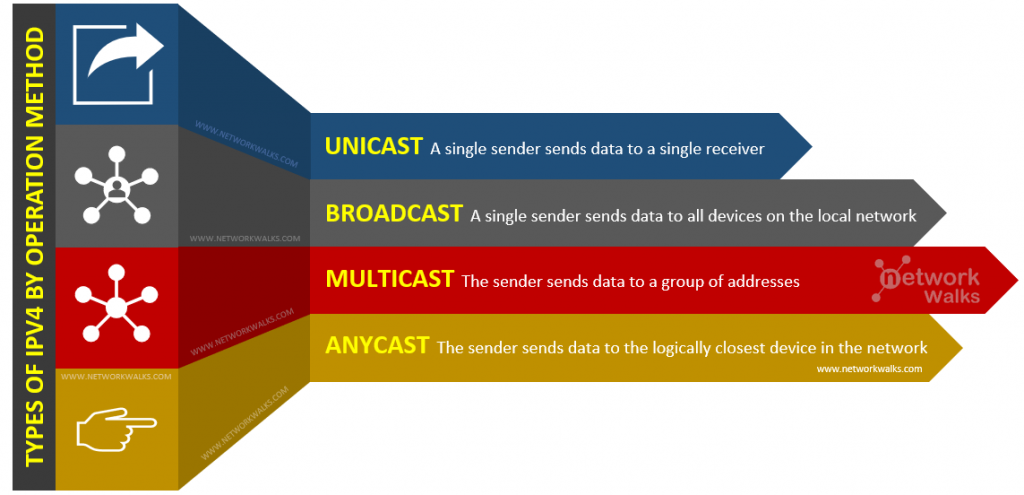
IP types can be classified into four types by way of operation which are listed in below:
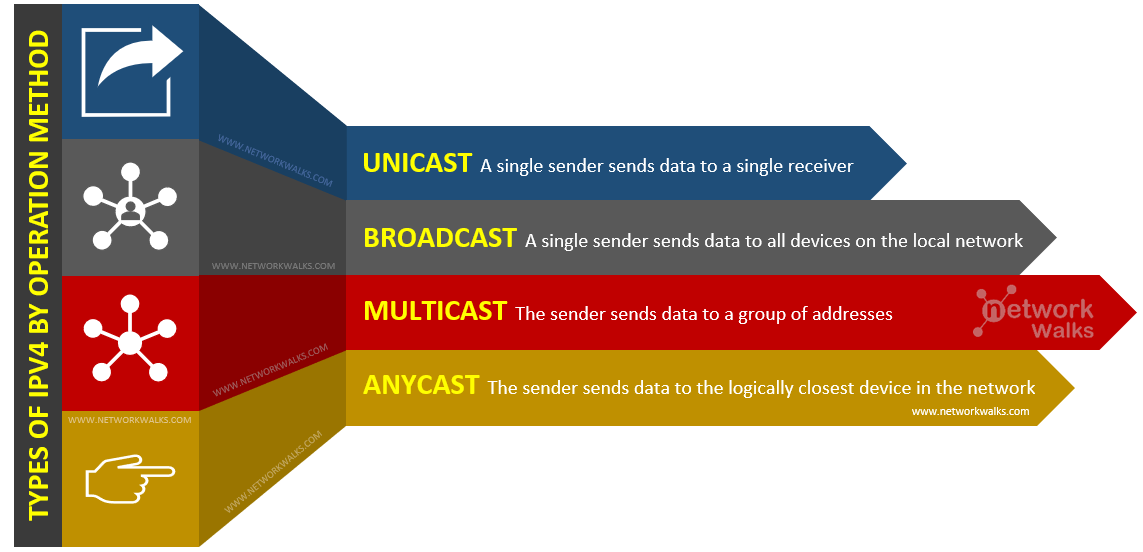
i. Unicast IP Address
This is the most common type of IP’s. A single sender sends data to a single receiver. It can be used for both sending and receiving.
ii. Broadcast IP Address
Send data to every other device on the local network.
*Broadcast is available only in IPv4 Addressing. IPv6 stopped the use of broadcast & replaced it with special multicast.
iii. Multicast address
“The source sends data from its unicast address to a group of addresses”
*Multicast addressing is usually executed through an intermediate Router.
iv. Anycast address
Anycast also sends data from one to many same as multicast & broadcast. But in Anycast, the data is not sent to all receivers. It is sent to just the logically closest device in the network.
B. Types of IP Address by IP versions
There are two versions of the Internet Protocol that are in common use, in the Internet today.
i. IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4)
The original version of IP is IPv4 which was first deployed in 1983. It is 32-bit number which is usually represented in dotted-decimal format. e.g. 192.168.1.1
ii. IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)
Then IPv6 was devised by IETF in 1995 due to rapid exhaustion of IPv4 address space. It is a 128-bit number.
C. Types of IP Address by Assignment Method
There are two types through which IP’s can be assigned to devices:
i. Static IP Address
Manually assigned Addresses by an admin.
ii. Dynamic IP Address
Automatically assigned addresses by a system or protocol.
D. Types of IP Address by Classes
Internet Protocol defines five classes of IP’s: class A, B, C, D, and E. Each class has a range of valid addresses assigned to it. The value of the first octet tells us the class to which it belongs to. First three classes (class A, B and C) are used for normal host & network addresses. The other two classes are used for other purpose.
* Class A addresses 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 cannot be used and is reserved for loopback and diagnostic functions.
| Class |
Address Range |
Detail |
Network / Host Part |
Default Subnet Mask |
| Class A |
1.0.0.1 – 126.255.255.254 |
Supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks |
N.H.H.H |
255.0.0.0 |
| Class B |
128.1.0.1 – 191.255.255.254 |
Supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks |
N.N.H.H |
255.255.0.0 |
| Class C |
192.0.1.1 – 223.255.254.254 |
Supports 254 hosts on each of 2Million networks |
N.N.N.H |
255.255.255.0 |
| Class D |
224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255 |
Reserved for multicast groups |
|
|
| Class E |
240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.254 |
Reserved for future use & R&D purposes |
|
|
E. Types of IP Address by Visibility
i. Public IP Address
Address which is used to locate the network devices on Internet or Public Networks
ii. Private IP Address
Address which is used to locate the network devices on Local or Private Network. These are the Private address ranges that belong to Class A, B & C.
| Class |
Private Networks |
Subnet Mask |
| Class A |
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 |
255.0.0.0 |
| Class B |
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 |
255.240.0.0 |
| Class C |
192..168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 |
255.255.0.0 |
You might also be interested in our free Online Quizzes on all IT topics including Cisco CCNA, Cyber Security, Python Programming, Linux & Ethical Hacking:
Free Online Quizzes (Best for Cisco CCNA, Huawei HCNA, N+)
You can also view free study notes (Cheat sheets) for long term memory:
Networkwalks Summary Cheatsheets
 “IP address is a unique number which is used to identify network devices in computer networks”.
An IP address mainly serves two functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. It is a logical numeric address that is assigned to every single computer, printer, switch, router or any other device that is part of a TCP/IP based network. The IP exists in every network, even only a pair of computers or a network of a large enterprise. Each computer, without exceptions, has its own unique address, if there is a connection to the network. Each of the computers in the network is related to IP. Moreover, there can not be two devices in one network with identical IP’s. But IP’s can be same in different networks.
IP’s as allocated step by step. Allocation starts with the request of the Internet provider to the national centers. They further distribute the received IP range of addresses among the customers. Customers can also become Internet service providers, in their turn, distributing the received IP’ss between their customers.
IP is like a phone number or your home address e.g. 1.1.1.1 or 192.168.0.1
“IP address is a unique number which is used to identify network devices in computer networks”.
An IP address mainly serves two functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. It is a logical numeric address that is assigned to every single computer, printer, switch, router or any other device that is part of a TCP/IP based network. The IP exists in every network, even only a pair of computers or a network of a large enterprise. Each computer, without exceptions, has its own unique address, if there is a connection to the network. Each of the computers in the network is related to IP. Moreover, there can not be two devices in one network with identical IP’s. But IP’s can be same in different networks.
IP’s as allocated step by step. Allocation starts with the request of the Internet provider to the national centers. They further distribute the received IP range of addresses among the customers. Customers can also become Internet service providers, in their turn, distributing the received IP’ss between their customers.
IP is like a phone number or your home address e.g. 1.1.1.1 or 192.168.0.1

