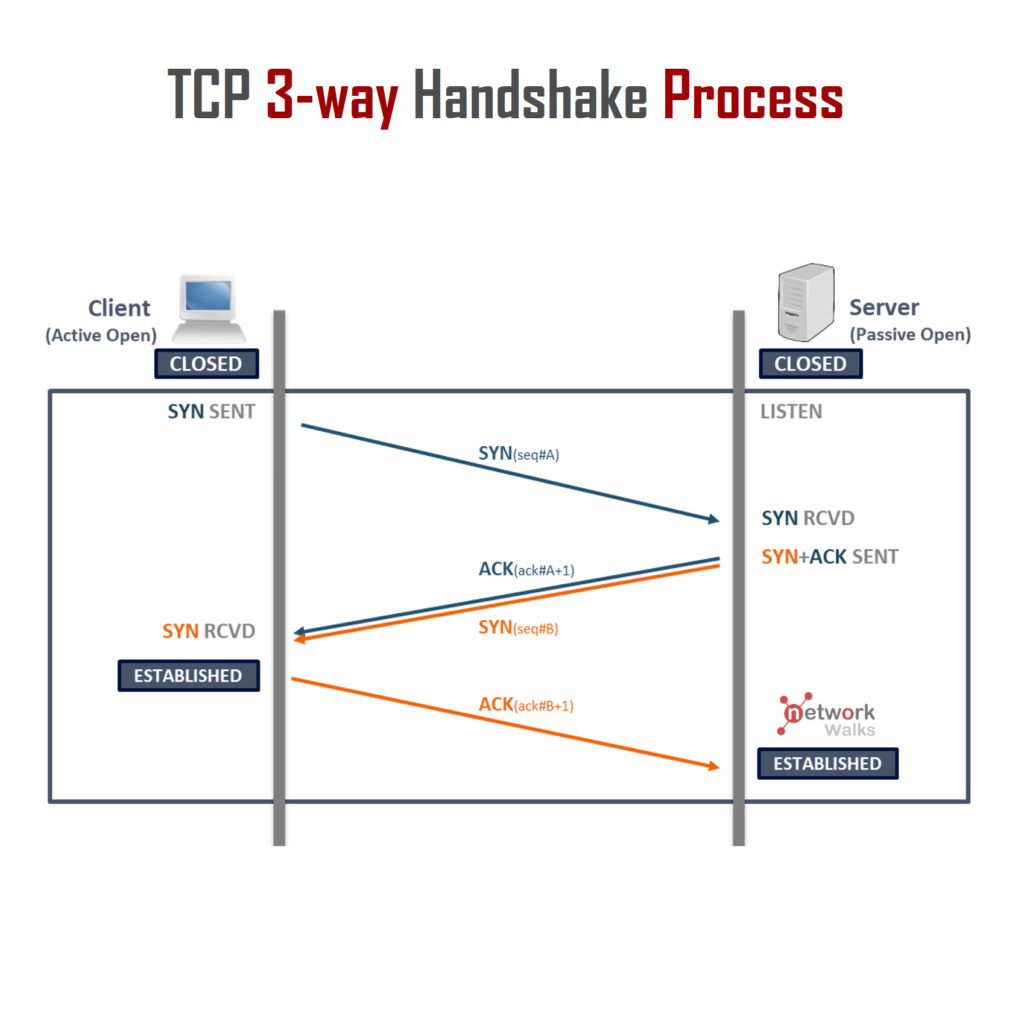
What is OSPF? OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is an open source dynamic routing protocol based on Link State Routing Algorithm for IP Networks. It has a Protocol Type/Class which is based on IP/Link-State. OSPF uses an Algorithm called SPF (Dijkstra) to determine the shortest path. It is an IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) Type of protocol and it uses Cost (Bandwidth) as its metric value. OSPF has 5 no. of packet types and has an Admin Distance of 110. It has a Reference Bandwidth of 108 and has a defined Standard of IETF RFC2328 (OSPFv2), IETF RFC2740 (OSPFv3/IPv6) for OSPF Read More …