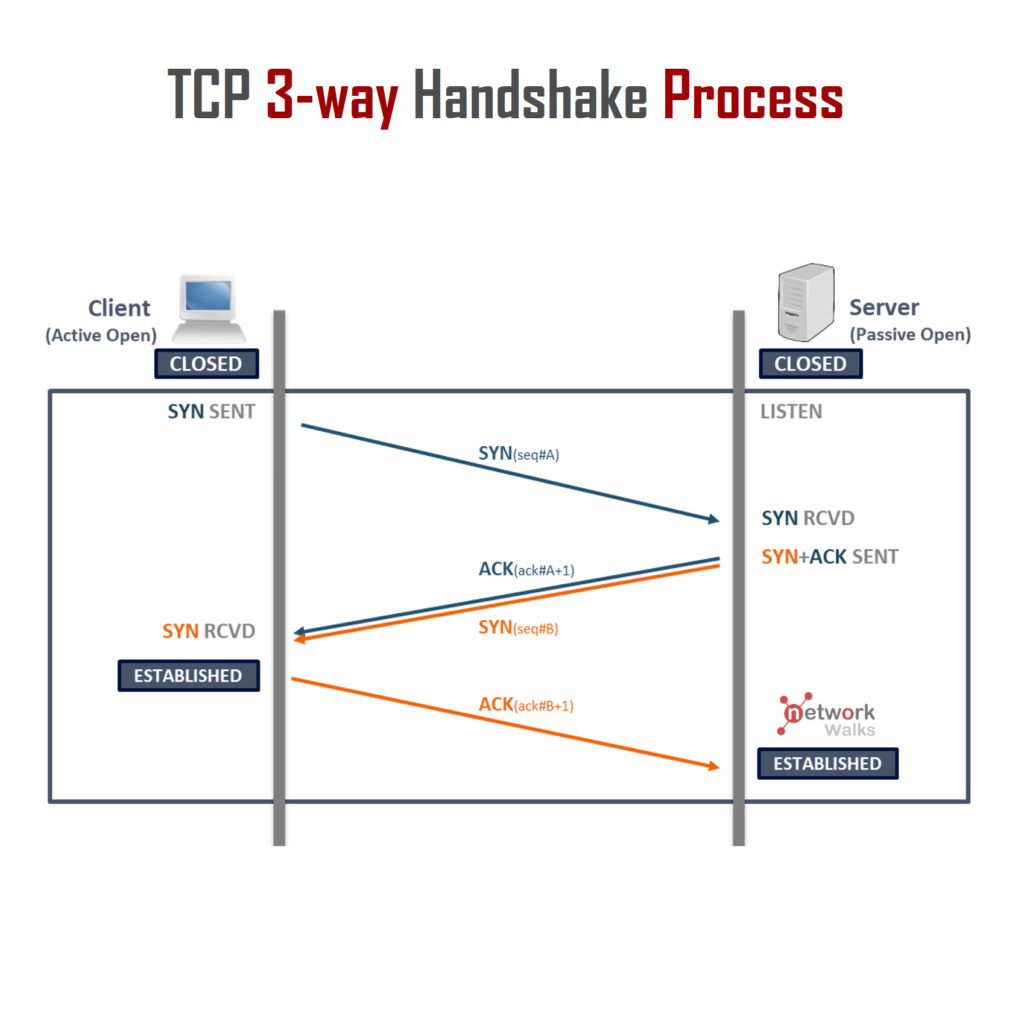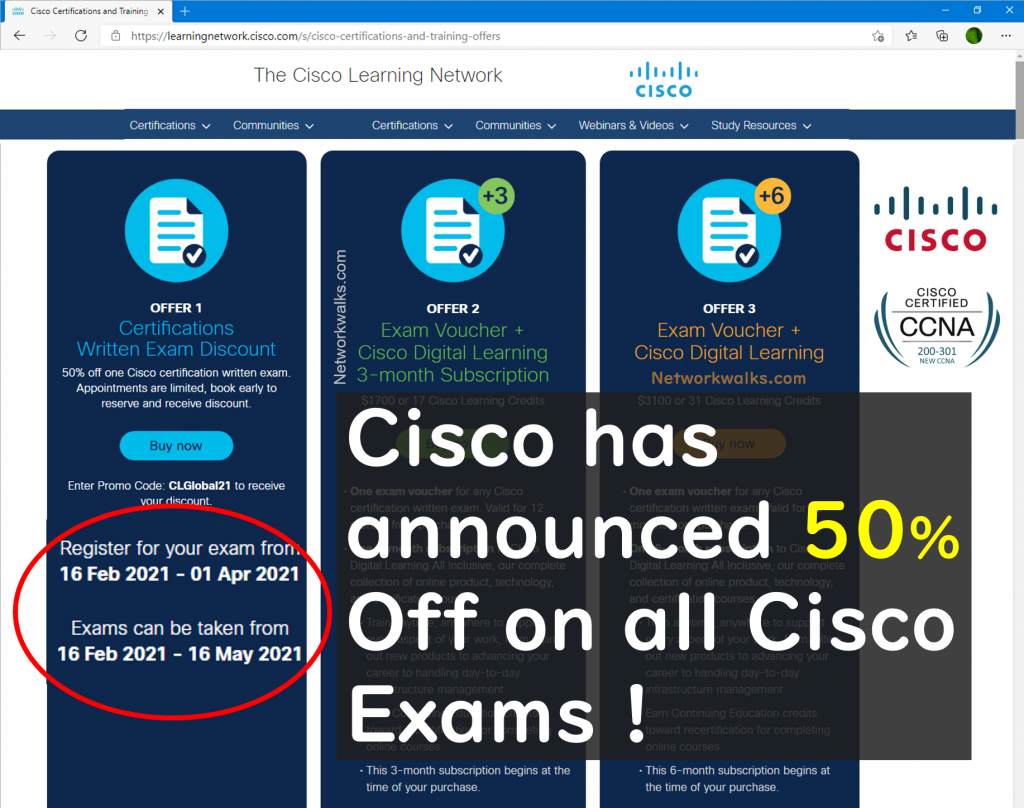
Cisco has officially announced a 50% off discount on all exam fee today which is valid till 16-May 2021. This is a very Good News for all students who have been planning to attempt their Cisco CCNA, CCNP-1 OR ENCOR exam recently. So, if you were planning to attempt the exam, then this is the best opportunity for you to avail this cisco discount offer. We have prepared a short video on this, plz watch it now. Official Cisco website (as shown in this video): https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/s/cisco-certifications-and-training-offers Please read all detail yourself from above Cisco official website. Below are some important Read More …